Home » News & Articles » Plate Thickness Variations
With the increased capability of hot mills to roll heavy coil (up to ½” thick), has come an increased awareness of the thickness variations that can be present in conventional discrete hot rolled plates.
In the past, plate products with a thickness of 3/16″ or more were produced as individual pieces, commonly 96″ wide or even wider in some instances. When these plates are rolled, the rolls can deflect, resulting in a crown shape on the plate where the thickness in the middle is greater than at the edges. The thickness tolerances for these plates are defined in ASTM A480, Table A2.17. The minus tolerance of 0.010″ applies to all thicknesses at all points. However, the plus tolerances differ. The table shows that the listed plus tolerances, for example, 0.050″ on a 96″ wide 1/4″ plate, apply only to the longitudinal edges of the rolled plate as measured at least 3/8″ from the edge and not more than 3″ from the edge. This specification didn’t provide any plus tolerance requirement on the middle of the plate except for 3″ on either edge.


Over time, ASTM revised A480 to include upper limits on thickness greater than 3” away from the longitudinal edge. Once the change to the specification was adopted, lengths greater than 3” away from a longitudinal edge could not exceed twice the tolerance of table A2.17. In the case of the 1/4″ plate mentioned above, while the zone along the original longitudinal edge must meet a 0.050″ maximum, the center of a 1/4″ plate can measure as much as 0.350″. As plate production satisfied these limits, no change in production needed to be made. The standard also notes that the edge thickness tolerances in Table A2.17 apply to as-produced mill plates, not to smaller pieces cut from these plates. The revision to the standard ensures that end users are aware of what the upper limits might be.
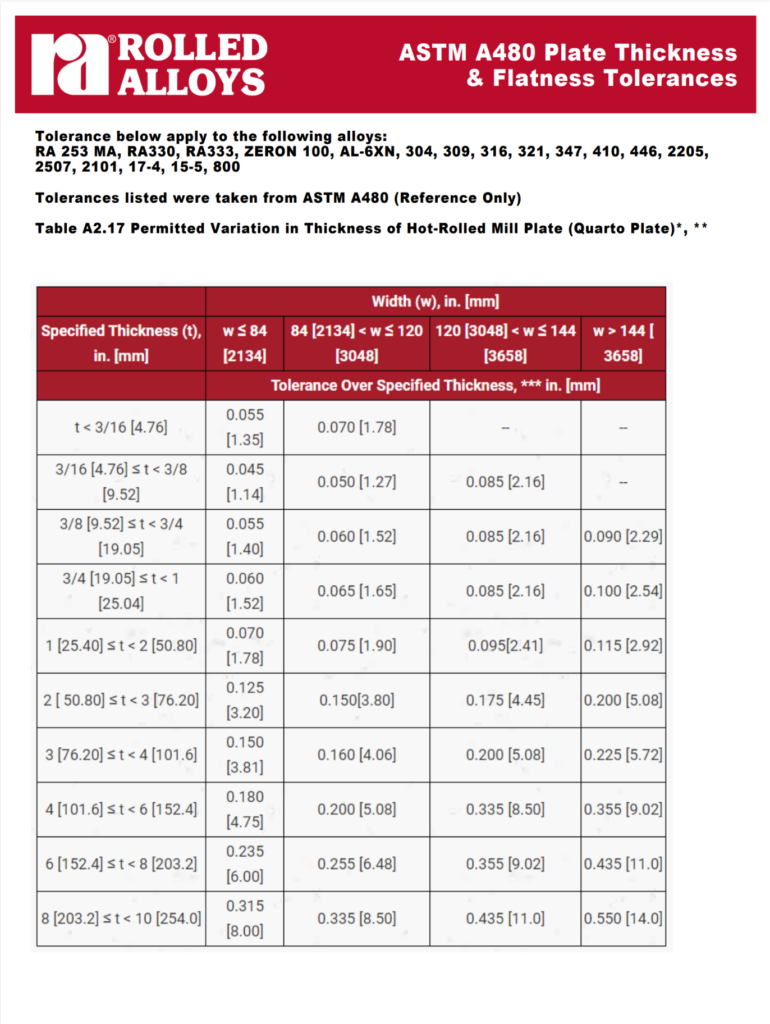
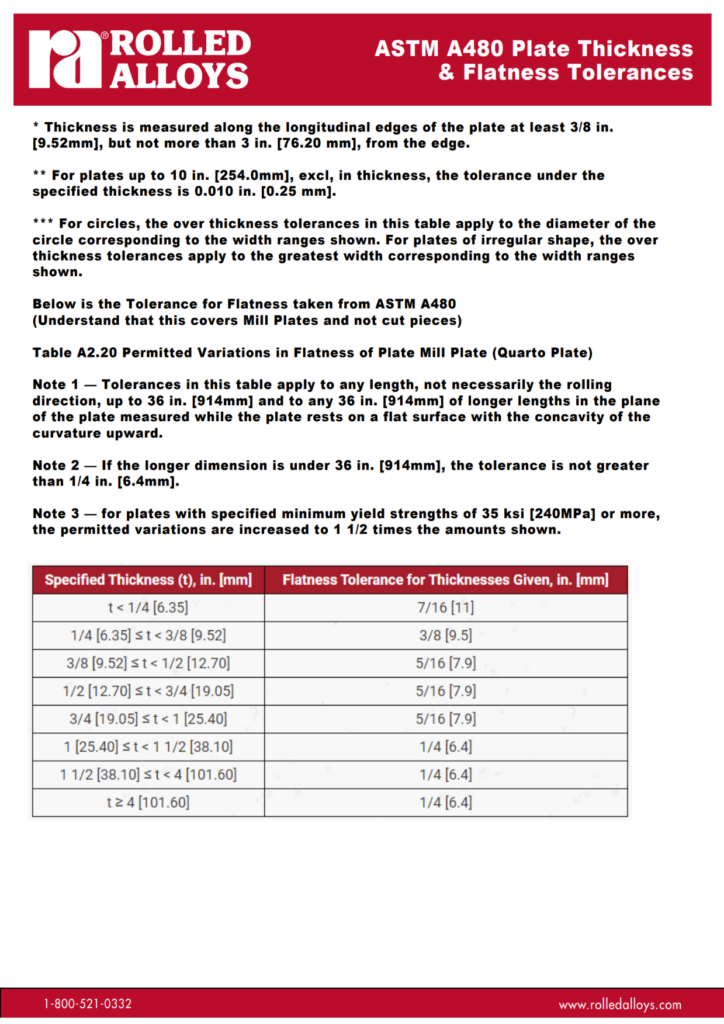
Table A2.17

It is generally not a problem for most users to handle a heavier stainless steel plate, and it can even be to their advantage. The pricing of stainless steel plates is typically based on their theoretical weight, area, or per piece, making it independent of thickness variations. In some cases, the extra thickness provided by the crown can offer more stock for a cleanup allowance without requiring the purchase of a heavier gauge. However, plate produced from coil may have less of a crown, making it a disadvantage for machinists. Machine shops that perform machining operations on blocks of material cut from the center of a plate may encounter extra machining due to the heavier thickness at the center. For instance, a 3/8″ thick plate may be as thick as 1/2″ in the center.

The Value of Cut Part Inspection
Modern metal fabrication demands fast, accurate cut metal inspection to keep up with high-volume production and tight tolerances

RA 253 MA® vs 309/310
Comparing RA 253 MA® and 309/310: Performance, Durability, and Applications

5-Axis Waterjet Beveling
A 5-axis waterjet cutting machine is an advanced CNC cutting tool that uses a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasive (usually garnet) to cut
Never Miss an Update - Subscribe Today!
Get application insights, material guides, and technical answers straight from the leaders in high-performance alloys.
Share:
QUOTE, BUY, TRACK
We make it easy to get instant pricing and purchase your metal at the click of a button. Track your order progress, get notified when it ships, and follow your shipment online until it’s delivered. It’s that easy!
Latest Articles
The Value of Cut Part Inspection
Modern metal fabrication demands fast, accurate cut metal inspection to keep up with high-volume production and tight tolerances
RA 253 MA® vs 309/310
Comparing RA 253 MA® and 309/310: Performance, Durability, and Applications
5-Axis Waterjet Beveling
A 5-axis waterjet cutting machine is an advanced CNC cutting tool that uses a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasive (usually garnet) to cut through metals and other materials.
AL-6XN Case Study
AL-6XN® Case Study AL-6XN® Resisted corrosive environments at indianapolis power and light for over 5 years Specifications UNS: N08367 ASTM: B 688, A
A Smarter Way to Order Metal Online
Introducing updates to the Rolled Alloys eCommerce experience designed for speed, clarity, and control.


